Evaluation of Nigeria’s Sustainable Development Goals Agenda 2030 using mathematical programming
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59543/ijsdg.v1i.14219Keywords:
Sustainable Development Goals; Societal Sustainability; Goal Programming; COVID-19; Nigeria Vision 2030Abstract
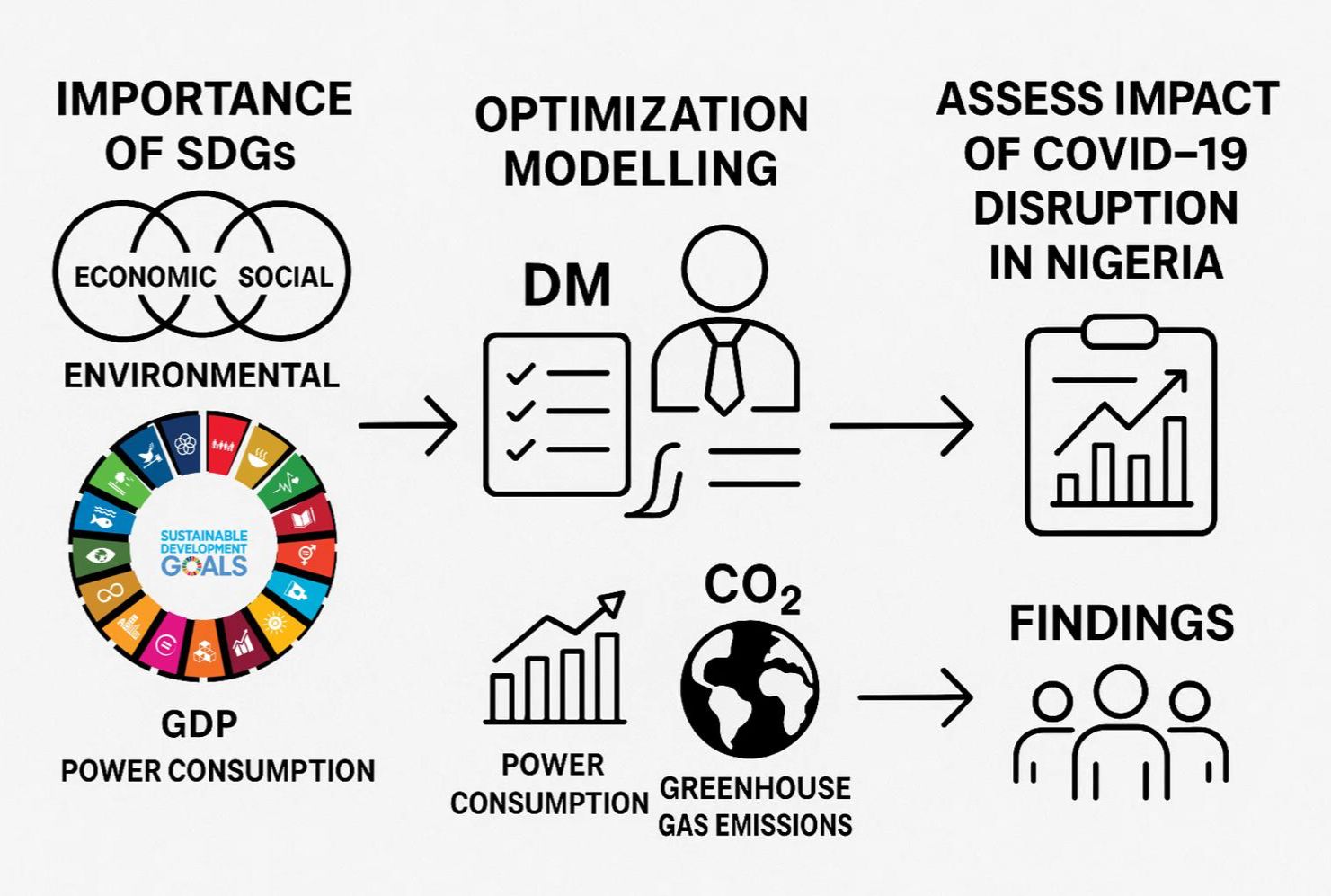
It is impossible to overstate the importance of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to every society. Connecting economic, social, and environmental sustainability, the SDGs have 17 interconnected goals with 269 target indicators. To achieve the SDGs cost-effectively and efficiently, decision-makers (DM) and policymakers seek rigorous and robust decision-making tools like optimization modelling. This study considering the disruption of COVID-19 on the economic and sustainability issues globally, assessed the trend and progress associated with the SDGs target of Nigeria. The research utilized quantitative and qualitative data on critical factors such as Nigerian growth domestic product (GDP), power consumption by economic contributing sectors, employment, and greenhouse gas emissions, and considered in the modelling. The findings indicated areas where the authorities are performing well and where it needs to assert more effort strategically to address the country’s economic challenges for socioeconomic growth and sustainability. The concept of the study can be replicated in other countries with some slight modification in the modeling and problem formulation. Future scope can explore the African vision 2040, using different concept.